| Configuring Route Summarization |
| (perform on each router) |
| configure terminal |
| interface serial0/0 |
| ip summary-address eigrp 1 [address][subnet mask] |
| * Routers now only advertise the "summarized" route to other routers |
| * show ip route will say "Variably subnetted" to indicate multiple masks are used. |
| * Summarized routing table includes network id with outgoing interface set to null0, meaning a packet can be sent to correct network, but no matching subnet exists, packet is discarded. |
VLSM Requirements: subnets do not overlap, and the routing protocol supports it.
Interior IP Routing Protocol VLSM Support
| Routing Protocol | Support VLSM |
| RIPv1 | No |
| IGRP | No |
| RIPv2 | Yes |
| EIGRP | Yes |
| OSPF | Yes |
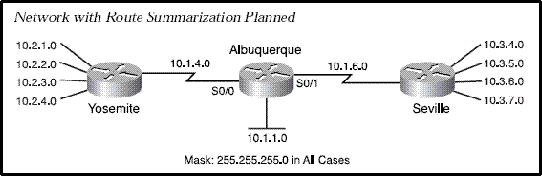
| Finding the "Best" Summary Subnet Mask |
| 1. Write down all subnets in binary form. |
| 2. Find where the first difference occurs. |
| 3. Use that subnet mask. |
| Example: |
| 10.2.1.0 = 0000 1010 0000 0010 0000 0001 0000 0000 |
| 10.2.2.0 = 0000 1010 0000 0010 0000 0010 0000 0000 |
| 10.2.3.0 = 0000 1010 0000 0010 0000 0011 0000 0000 |
| 10.2.4.0 = 0000 1010 0000 0010 0000 0100 0000 0000 |
| Set the values that aren’t bold to 1, set all other values to 0, and use that as your mask: |
| 255.255.248.0 |
Classless and Classful Routing Protocols
Classful don’t transmit the subnet mask information in updates.
Classless do transmit the subnet mask information in updates.
Autosummarization: In classful routing, uses Static Length Mask (uses the traditional Class A, B, and C masks).
- RIP and IGRP perform this by default (can’t disable)
- RIPv2 and EIGRP, can either be enabled or disabled
| Contiguous Network: Single Class A, B, or C network for which all routes to subnets of that network pass through only other subnets of that same single network |
| Discontiguous Network: Only routes to one subnet pass through route of another subnet of a different network. |
| Analogy Lower 48 states are contiguous because you can drive to any point without needing to go through another country (subnet/network). To get from Alaska to one of the lower 48 states, you must go through Canada (a separate network), so it is discontiguous. |
** Classful protocols do not support discontiguous networks. **
To migrate from classful to classless
Configure using classless protocol, disable autosummarization.
l and Classless Routing
| Classful & Classless Routing Default Routes are best when only a single path exists to a part of the network. |
| Also called Gateway of Last Resort |
| Configure: |
| ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 [IP address of next hop] |
| -or- |
| : ip default-network [address] |
| In show ip route command, * (asterisk) denotes it is a candidate for default route. |
| 'Toggle between classful/classless: 'ip classless and no ip classless |
| Classful Logic |
| Match network in routing table |
| Look up specific subnet |
| If exists, forward, otherwise, discard |
| Classless Logic |
| Lookup specific subnet |
| If exists, forward, otherwise, send to default gateway |
No comments:
Post a Comment